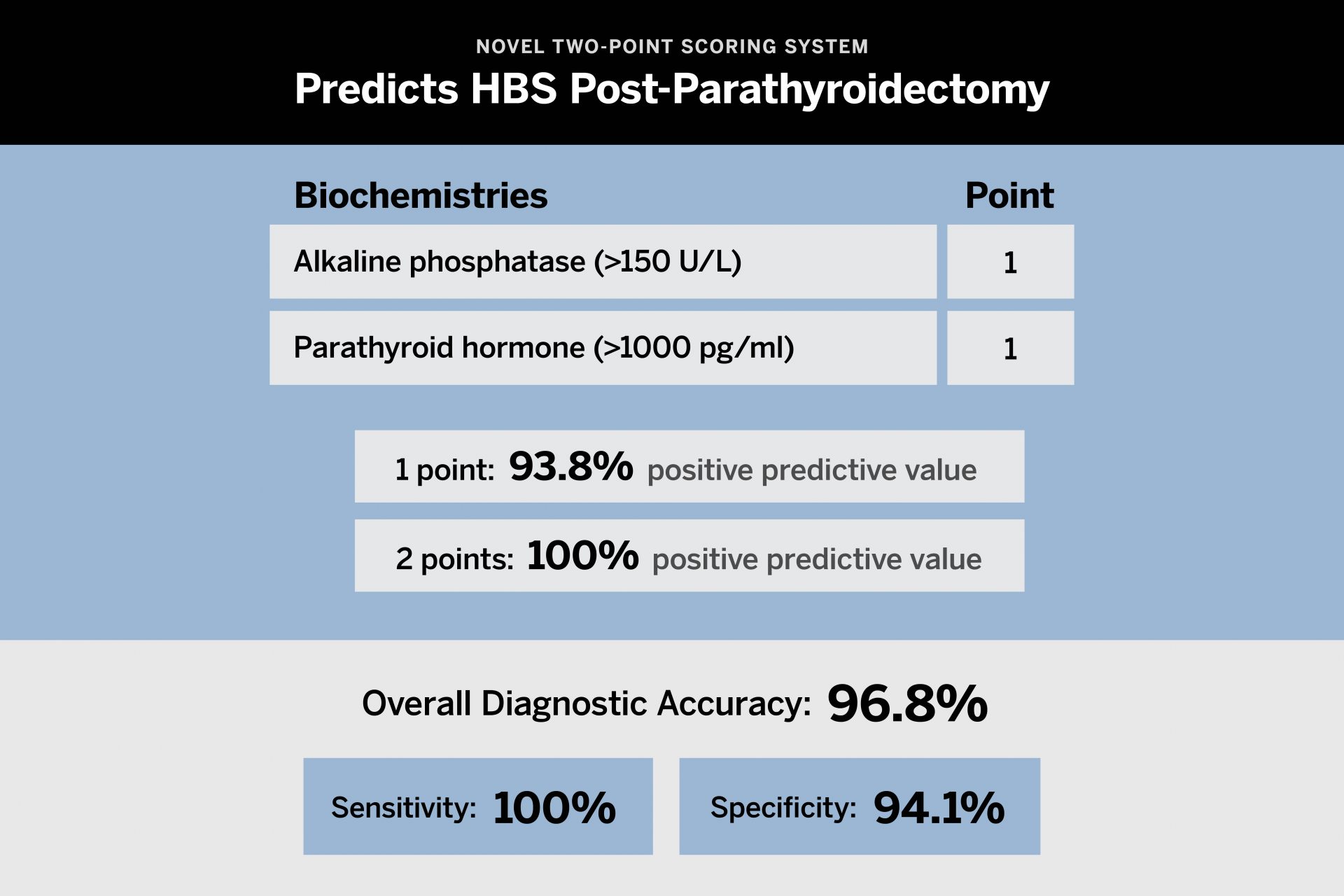
In a recent study published in Endocrine Practice, NYU Langone Health researchers identified two preoperative variables—serum parathyroid hormone (PTH) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP)—as being significantly associated with hungry bone syndrome (HBS) after parathyroidectomy for renal hyperparathyroidism.
The team drew upon a decade of data to analyze the risk factors of postsurgical HBS, ultimately building a simple, 2-point scoring system based on PTH and ALP levels; the predictive algorithm identifies patients at high risk of HBS with nearly 97 percent accuracy.
“Pairing this scoring system with a standardized perioperative treatment protocol has the potential to really reduce the incidence and/or severity of HBS,” says endocrinologist Melissa Sum, MD, lead author on the study. Endocrine surgeon Insoo Suh, MD, served as a coinvestigator of the study.
“Pairing this scoring system with a standardized perioperative treatment protocol has the potential to really reduce the incidence and/or severity of HBS.”
Melissa Sum, MD
HBS, characterized by significant hypocalcemia, can occur in the postoperative period following parathyroidectomy. Rapid diagnosis and management of HBS is imperative due to the possibility of life-threatening complications, including cardiac arrhythmias and generalized seizures.
While previous reports have identified markedly elevated PTH and ALP to be associated with HBS development, the model is unique in its high accuracy, simplicity and utility in predicting patients at high risk of HBS, particularly in the preoperative setting.
“This is a very user-friendly tool to identify HBS that should significantly inform and improve post-operative care by enabling prevention and preemptive treatment strategies.”
Insoo Suh, MD
“This is a very user-friendly tool to identify HBS that should significantly inform and improve post-operative care by enabling prevention and preemptive treatment strategies,” Dr. Suh says.
Taken together, Dr. Sum says the findings support the utility of these metrics in future attempts to create standardized perioperative treatment protocols and electronic medical system alerts.
“Our model predicts HBS in the preoperative setting with very high accuracy and has immense practical application,” she says.