For patients with diabetes undergoing a primary total knee arthroplasty (TKA), insufficient glycemic control before, during, and after surgery can lead to complications such as surgical-site infections and poor wound healing. Dexamethasone can reduce postoperative pain, nausea, and vomiting. Like other corticosteroids, however, dexamethasone can increase blood glucose levels, raising concerns about whether a second dose administered to diabetic patients undergoing TKA might complicate their recovery.
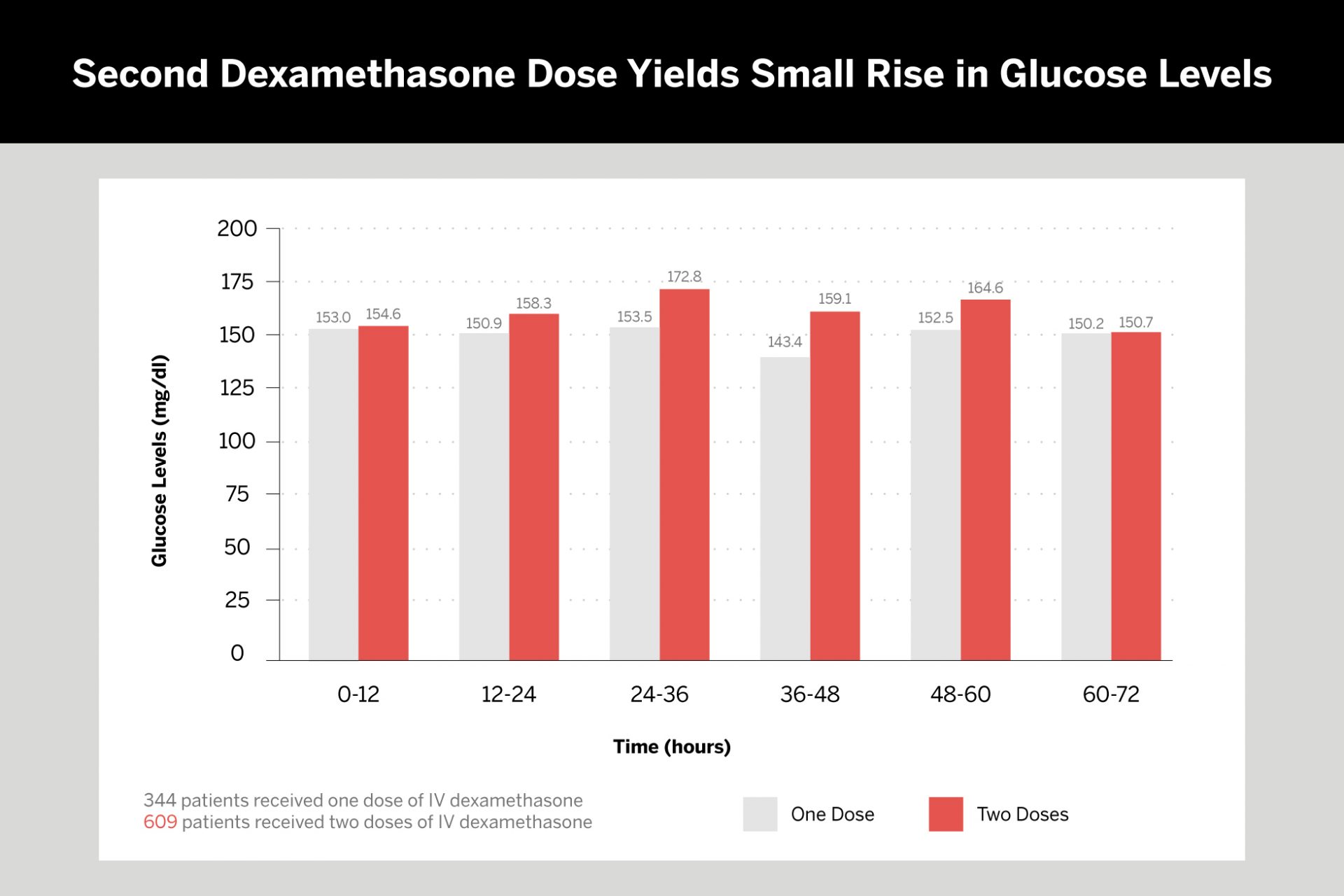
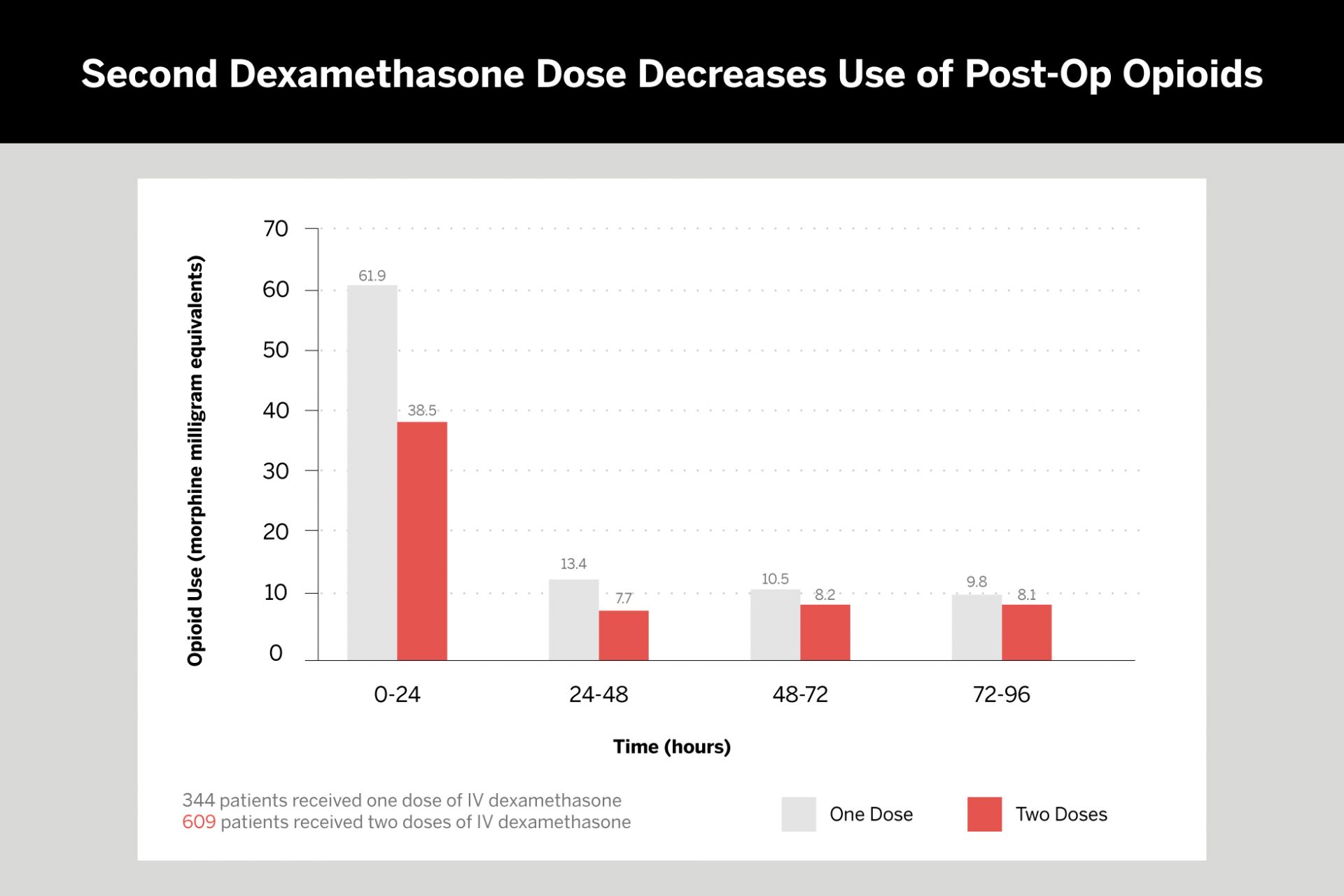
In a retrospective study of 953 TKA patients, NYU Langone Health researchers found that a second dose of dexamethasone temporarily increased glucose levels compared to only one dose. In both groups of patients, however, average glucose levels never exceeded the 200 mg/dl threshold for postoperative wound complications. Furthermore, the two-dose group consumed fewer opioids in the first 48 hours post-surgery. The study revealed no difference in infection rates, delayed wound healing, or other complications within the 90-day postoperative period.
“Using dexamethasone for primary total joint replacements, even in diabetic patients, is both safe and effective in reducing pain and reducing inpatient opioid usage without a substantial detrimental effect on maintenance of blood sugar.”
Joshua C. Rozell, MD
Orthopedic surgeon Joshua C. Rozell, MD, won the best podium presentation award at the annual meeting of the American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons in 2022 for summarizing his team’s initial findings. “My recommendation would be that using dexamethasone for primary total joint replacements, even in diabetic patients, is both safe and effective in reducing pain and reducing inpatient opioid usage without a substantial detrimental effect on maintenance of blood sugar,” he says.
Dr. Rozell cautions that diabetic patients must be closely monitored for blood glucose levels. “Clinicians should make sure to utilize a multimodal pain protocol with various non-opioid analgesics that can synergistically work to decrease pain level after surgery,” he adds. The study, he says, affirms that despite its transient effect on glucose control, dexamethasone can be a safe and effective part of that analgesic mix, even for diabetics.