A 62-year-old male with obstetric brachial plexus injury (OBPI) from Erb’s palsy sought surgical treatment after nonoperative approaches failed. The primary goal was pain reduction, with shoulder function improvement as a secondary goal. Preoperative imaging showed humeral head impaction, severe post-traumatic glenohumeral osteoarthritis, and severe glenoid dysplasia. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty (RTSA) with glenoid bone graft/augment was chosen for treatment.
Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty for Post-Traumatic Arthritis in a Patient with Obstetric Erb’s Palsy
Dr. Joseph Zuckerman led the surgical team in performing the operation on a 62-year-old male.
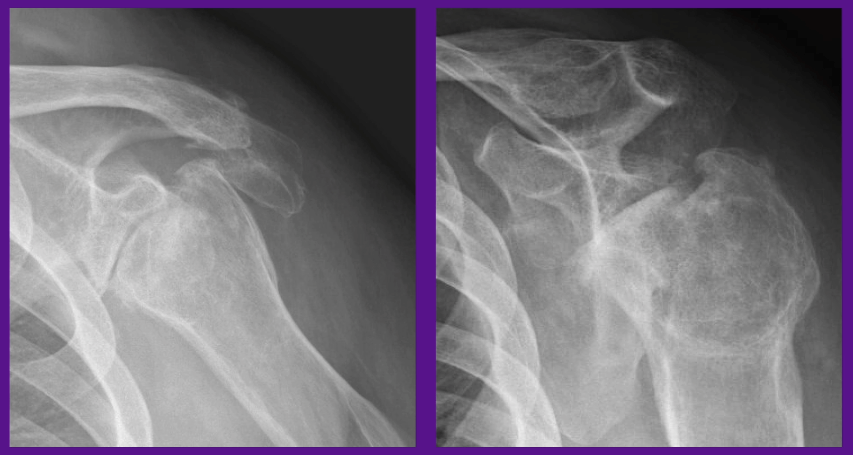
Preoperative imaging from the case: anterior–posterior view and trans-scapular view. Source: NYU Langone Health
The Best Experts and Latest Breakthroughs
Select your specialty to receive updates on our pioneering research, innovations, expert perspectives, case studies, practice-changing medicine, and more.